Your Time has Finished
Which UCAT Exam
are you sitting?
Loading...
QR-5 Percentages & Proportion – Homework
Your Score:
Average Score of All Users:
You performed better than of students
Section Breakdown
| Your Score | Average of all Users | Percentile | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Percentages & Proportion |
Percentages & Proportion
Your score:
Average score:
You performed better than of students
Time to put your knowledge about proportion questions to the test!

This is the daily schedule that Harry has stuck to on Monday to Friday for the past six weeks whilst working from home. He has always taken Saturdays and Sundays off from work.
Explanation
Answer: D
Explanation:
1. Convert the units into metres and seconds and find the average speed.
1 hour = 60 minutes = 60 x 60 seconds = 3600 s
10 km = 10,000 m
So in metres per second:
10000 / 3600 = 2.777… = 2.8 m/s
Common trap: Notice that the answers are all in m/s. He has run at 10 km/h so make sure that you don’t slip up and pick answer E without thinking.

This is the daily schedule that Harry has stuck to on Monday to Friday for the past six weeks whilst working from home. He has always taken Saturdays and Sundays off from work.
Explanation
Answer: C
Explanation:
1. Work out his old cost and his new cost and find the percentage difference
His old costs were the meal deal and coffee:
2.75 + 3.00 = £5.75
His new costs are:
1.50
Use the formula:
Multiplier = New Value / Old Value
Multiplier = 1.50 / 5.75 = 0.26….
0.26… = 74% percentage decrease – Option C.
Timing Tip: Percentage decrease is one of the most commonly tested skills in UCAT Quantitative Reasoning. Get to grips with the multiplier method to save precious time.
Timing Tip: Note that the percentage difference will be same for one day as for 5 – there is no need to work out the values for 5 days’ worth of purchases.
 rithy
Medicmind Tutor
rithy
Medicmind Tutor
Fri, 23 Jul 2021 11:29:04
how .26 = 74 %
 x
Medicmind Tutor
x
Medicmind Tutor
Fri, 27 Aug 2021 06:20:43
how is .26 74 %
 Danielle
Medicmind Tutor
Danielle
Medicmind Tutor
Fri, 03 Jun 2022 13:42:39
I didn't understand the working out shown above. My method of getting to the answer was I did £2.75 + £3.00= £5.75 For homemade £1.50 Across the span of the working week Mon to Fri (Harry's working days) Homemade= £1.50 x 5 = £7.50 Meal deal = £5.75 x 5 = £28.75 28.75-7.50 / 28.75 x100 = 73.9 % rounded off gives 74%.
 Chef Doc
Medicmind Tutor
Chef Doc
Medicmind Tutor
Thu, 21 Jul 2022 13:44:59
Since we're finding the percentage decrease the equation is 100-(change in value/original value x 100). So 100-(1.5/5.75 x100)= 73.9 which is just 74%
 oh
Medicmind Tutor
oh
Medicmind Tutor
Wed, 29 Mar 2023 19:49:53
oh i get it smh. for some reason they didn’t want to type it all out so allow me to finish it off for them. 1.50 / 5.75 = 0.26 0.26 x 100 = 26% 100% - 26% = 74% decrease. voila.
 Anon
Medicmind Tutor
Anon
Medicmind Tutor
Fri, 09 Jun 2023 03:28:56
"Across the a working week" is kind of confusing. Why not just say "What is the percentage decrease in the cost of a homemade lunch"?

This is the daily schedule that Harry has stuck to on Monday to Friday for the past six weeks whilst working from home. He has always taken Saturdays and Sundays off from work.
Explanation
Answer: C
Explanation:
1. Find the speed at which he is typing and the time he is typing for.
He is working at 67.5% of his maximum of 80 words per minute.
67.5% of 80 = 54 words per minute.
He is typing for 4 and a half hours apart from a half-an-hour zoom call and 10 minutes total in breaks.
This means that, in minutes, he was working for 270 – 30 – 10 = 230 minutes.
This means he typed:
230 x 54 = 12,420 words in his pre-lunch session.
Common Trap: Note that he does not type at his maximum speed in this work session – if he did then the answer would be E.
 E
Medicmind Tutor
E
Medicmind Tutor
Mon, 02 Aug 2021 18:58:55
I got the right answer in the end, but I found it a bit confusing when it says 'in the morning' as I'd class that until 12pm, would be better worded as before lunch

This is the daily schedule that Harry has stuck to on Monday to Friday for the past six weeks whilst working from home. He has always taken Saturdays and Sundays off from work.
Explanation
Answer: D
Explanation:
1. Find the eco-shower’s water use and thus the other showers’ use.
The eco shower uses 25 ml per second.
If Harry showers for half the time between arriving home and starting work, he showers for 15 minutes.
15 x 60 x 25 = 22,500 ml.
This is 20% less than other models:
Use the formula:
New Value / Multiplier = Old Value
The multiplier for a 20% decrease is 0.8:
22500 / 0.8 = Old Value
28125ml = Old Value
In litres:
28125 / 1000 = 28.125L – answer D.
Common Trap: Remember when working out a percentage decrease to divide by the percentage decrease as a multiplier rather than by multiplying by the same percentage as a percentage increase. Using a multiplier of 1.2 would give 27L – lower than the true original value.
 sedra
Medicmind Tutor
sedra
Medicmind Tutor
Fri, 23 Jul 2021 22:17:54
someone tell me how do i freaking avoid careless mistakes !!!!
 anoymous
Medicmind Tutor
anoymous
Medicmind Tutor
Sat, 10 Sep 2022 10:26:51
i am not terrible at maths but the ucat makes me feel dumb ;(
Explanation
Answer: D
Explanation:
1. Find the average weekly sales in Year 1
123,545 in 5 weeks
123,545/5 = 24709 a week
2. Find the average weekly sales in Year 2 and thus the total:
New Value = Old Value x Multiplier
24,709 x 1.25 = 30,886.25
The festival ran for 8 weeks so:
30,886.25 x 8 = 247,090 tickets total – option D.
 Sophie Fowler
Medicmind Tutor
Sophie Fowler
Medicmind Tutor
Sun, 11 Jul 2021 13:09:24
The question doesn't ask for average weekly ticket sales.
 anon
Medicmind Tutor
anon
Medicmind Tutor
Wed, 20 Jul 2022 05:48:29
The question doesn't ask for average weekly ticket sales.
 Daanyaal
Medicmind Tutor
Daanyaal
Medicmind Tutor
Sun, 07 Aug 2022 06:32:56
how do we estimate the value of the multiplier? plss let me know
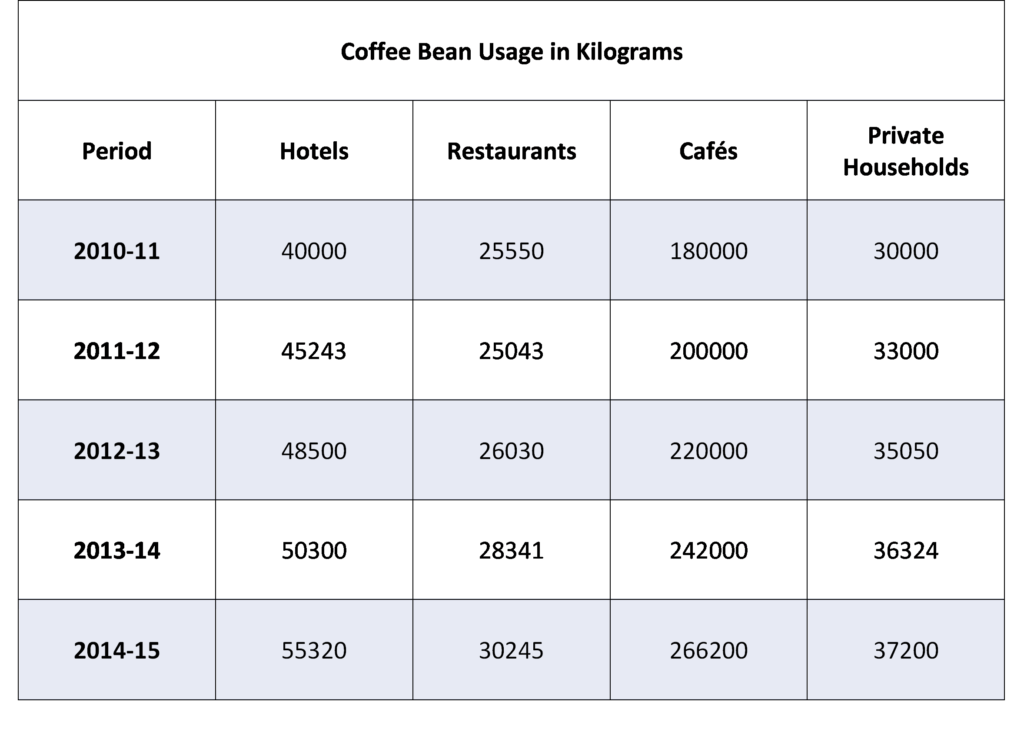
● All figures in the table are in kilograms.
● 1 ml water = 1g
Explanation
Answer: C
Explanation:
1. Find the coffee bean usage in cafés as a percentage of all the coffee beans used.
Beans in cafés: 242,000
Beans in total: 242000 + 50300 + 28341 + 36324 = 356965
242000/356965 = 0.6779… = 67.8%
Timing Tip: For this question, you could round the values to 50,000, 28,000 and 36,000 and you would still get an answer (67.9%) which clearly indicates option C
Timing Tip: Using rounded numbers, you could do some of these additions in your head or with the help of the scratch pad: 242 + 50 + 28 + 36 will tell you the number of thousands without having to type each number out in full.
Top Tip: Make sure to familiarise yourself with the scratchpad and calculator using the UCAT official website. You don’t want the first time you are using it to be in the real exam.

● All figures in the table are in kilograms.
● 1 ml water = 1g
Explanation
Answer: C
Explanation:
1. Find the sum of all the values in the table:
40000 + 25550 + 180000 + 30000 + 45243 + 25043 + 200,000 + 33000 + 48500 + 26030 + 220000 + 35050 + 50300 + 28341 + 242000 + 36324 + 55320 + 30245 + 266200 + 37200 = 1654346 Kg
2. Find the mean annual use:
The mean use = Total use in the period/Number of years
1654346/5 = 330869.2 so 330869 to the nearest kilogram.
Top Tip: Identify early on that this question is asking for the mean of all the values. Furthermore, the answer options are close together so it is clear that precision will be required. The best candidates will spot this is a potential timing trap and be strict about keeping to the 40s limit.
 A
Medicmind Tutor
A
Medicmind Tutor
Sun, 31 Jul 2022 12:17:32
id skip this question. no way I can do it under 40s
 brain gal
Medicmind Tutor
brain gal
Medicmind Tutor
Mon, 19 Sep 2022 12:56:38
how cud they expect us to do it in such a short time?

● All figures in the table are in kilograms.
● 1 ml water = 1g
Explanation
Answer: A
Explanation:
A is incorrect. Between 2010-11 and 2011-12 the increase was 200,000/180,000 = 1.11 which is an 11% increase not 10%. The other values are 10% increases but not the first period.
B is true. It fell between 2010-11 and 2011-12 but rose every other year.
C is true. 50300/48500 = 1.0371… so a 3.7% increase
D is true. Only one value (restaurants in 2011-12) was lower than the year before. This decrease was more than compensated by the increases in values for the categories so this can be selected as true through inspection.
E is true. The percentage change is 10% in the first year, 6.2% in the second, 3.6% in the third and 2.4% in the final year.
Timing Tip: Options which only mention one of the categories should be targeted first – they only require the assessment of one subset of the data. This means D should be assessed last. From the others, it is clear that E would take the longest so should be a lower priority.
 Roshanak
Medicmind Tutor
Roshanak
Medicmind Tutor
Sun, 17 Jul 2022 13:58:34
It says A is wrong and B is correct in the explanation but the answer still shows up as A is correct
 Dan
Medicmind Tutor
Dan
Medicmind Tutor
Sun, 07 Aug 2022 06:53:47
plss fix the bug here, explanation contradicts the answer

● All figures in the table are in kilograms.
● 1 ml water = 1g
Explanation
Answer: D
Explanation:
1. Find the mass of coffee used in each ratio:
90% was used at a ratio of 1:18:
0.9 x 200,000 = 180,000
10% was used at a ratio of 1:20
0.1 x 200,000 = 20,000
2. Find the volume of coffee produced:
Find the volume of coffee made from this mass:
1g = 1ml
180,000 was used in the ratio 1:18 so:
180,000 x 18 = 3,240,000Kg so 3,240,000L
20,000 was used in the ratio 1:20 so:
20,000 x 20 = 400,000Kg so 400,000L
3,240,000 + 400,000 = 3,640,000L – D.
Common Trap: Remember that not all of the coffee will be made in the 1:18 ideal ratio. If this were true, the answer would be C.
 anon
Medicmind Tutor
anon
Medicmind Tutor
Mon, 23 Aug 2021 07:27:39
where's 200,000 coming from?
 anon
Medicmind Tutor
anon
Medicmind Tutor
Mon, 23 Aug 2021 07:28:17
nvm
 Lydia
Medicmind Tutor
Lydia
Medicmind Tutor
Sat, 04 Sep 2021 14:16:39
Hi there, why do you multiply 180000 by 18 when the coffee to water ratio is 1:18? Would it not be 180000x1/18?
 Beverly
Medicmind Tutor
Beverly
Medicmind Tutor
Mon, 06 Sep 2021 10:20:12
But you have to multiply by the coffee ratio value ie. 18 (and exclude water)
 anonymous
Medicmind Tutor
anonymous
Medicmind Tutor
Mon, 27 Jun 2022 06:14:01
Why is mass of coffee not being added when calculating volume
 rana
Medicmind Tutor
rana
Medicmind Tutor
Sat, 23 Jul 2022 17:01:21
shouldnt we be adding the ratio together then dividing it then multiplying it??

● All figures in the table are in kilograms.
● 1 ml water = 1g
Explanation
Answer: D
Explanation:
1. Find the total consumption from the old model:
40,000 + 25,550 + 180,000 + 30,000 = 275,550
2. Find the new values:
New value / Multiplier = Old value:
For the private households:
30000/1.15 = 26,086.9…
For the cafés:
180000/0.89 = 202,247.191…
3. Find the new total and percentage difference:
40000 + 25550 + 202247… + 26086.9… = 293,883…
293883… /275,550 = 1.0665 = 6.7% increase
Common Trap:A 11% underestimate means that the value given is 89% of the true value (11% percentage decrease to reach it) so to calculate the true value, divide by 0.89 rather than multiply by 1.11.
 dd
Medicmind Tutor
dd
Medicmind Tutor
Sat, 28 Aug 2021 00:37:10
how is 1.0665 equal to 6.7 % increase
 k
Medicmind Tutor
k
Medicmind Tutor
Wed, 15 Sep 2021 13:06:41
@dd, if you're converting to percentage, 100% = 1.00. For the change, 1.0665 - 1.00 = 0.0665 = 6.65% which is approximately 6.7%
 Makes no sense
Medicmind Tutor
Makes no sense
Medicmind Tutor
Thu, 21 Jul 2022 14:45:19
Why are we using an equation to find the old values if were looking for the new ones
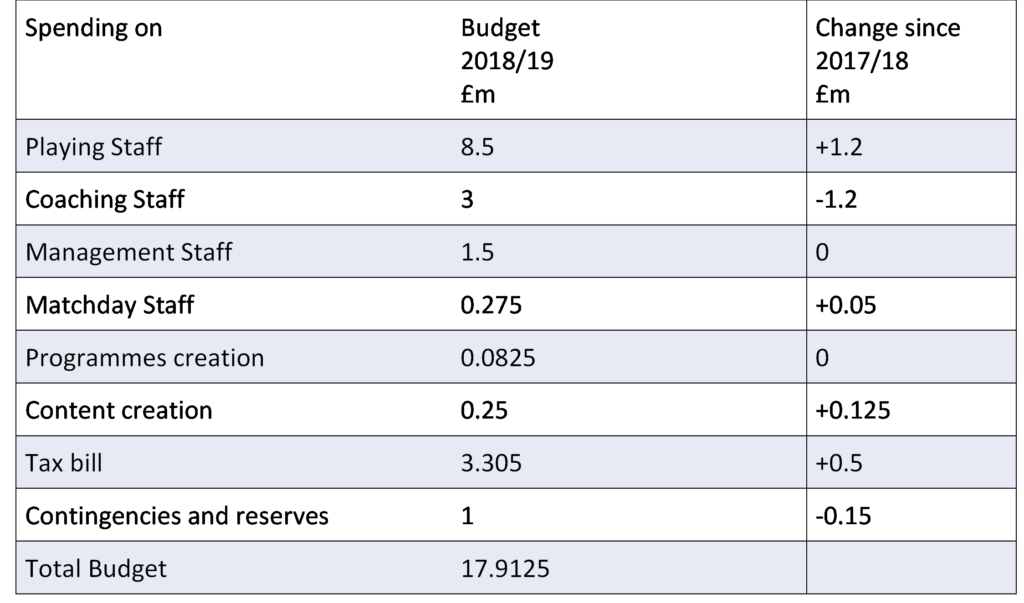
The budget for the Hornets, a premiership rugby club.
Explanation
Answer: E
Explanation:
1. Identify the data the question is asking for:
It has asked for the 2017/18 budget – this is not given directly in the question.
We are given the 2018/19 budget and how much more it is than the 2017/18 budget.
2. Take away the increases to find the previous budget:
17.9125 – 1.2 + 1.2 – 0.05 – 0.125 – 0.5 + 0.15 = 17.3875
Common trap: Remember to add on the values for when the budget has reduced from 2017/18 – two negatives make a positive.
 zohra
Medicmind Tutor
zohra
Medicmind Tutor
Tue, 18 Aug 2020 14:20:25
why is it -0.05 not +
 L
Medicmind Tutor
L
Medicmind Tutor
Sun, 01 Aug 2021 14:21:47
because +0.05 was the change from 2017/18 to 2018/19 and since we are working backwards to find the 2018/19 total from the 2017/18 total we do the inverse
The budget for the Hornets, a premiership rugby club.

Explanation
Answer: A
Explanation:
1. Find the playing staff budget as a proportion of the known 2017/18 budget:
Proportion for playing staff = Playing staff budget / Total budget
The total budget for 2017/18 was 17.3875
The playing staff budget was: 8.5 – 1.2 = 7.3
7.3/17.3875 = 0.4198… = 42.0%
 E
Medicmind Tutor
E
Medicmind Tutor
Mon, 02 Aug 2021 19:06:43
The explanation uses the total 2018/19 budget not 2017/18?
 Beverly
Medicmind Tutor
Beverly
Medicmind Tutor
Mon, 06 Sep 2021 12:01:00
It uses the 17-18 budget
 R
Medicmind Tutor
R
Medicmind Tutor
Thu, 07 Oct 2021 13:18:24
@E It uses the answer from the previous question from the previous question
The budget for the Hornets, a premiership rugby club.

Explanation
Answer: D
Explanation:
1. Find the wages in 2016/17
There was a 25% percentage decrease between 2016/17 and 2017/8:
Original Value x Multiplier = New Value
So
Wages in 2016/17 x 0.75 = Wages in 2017/18
Wages in 2017/18:
3 – -1.2 = 4.2 million
New Value / Multiplier = Original Value
4.2/0.75 = 5.6 million
Therefore, the bill in 2016-17 was £5.6 million – D
Common Trap: To calculate the original before a 25% decrease, divide by 0.75 rather than multiplying by 1.25.
 Alicia
Medicmind Tutor
Alicia
Medicmind Tutor
Mon, 20 Sep 2021 11:23:21
I solved it differently Take the wages in 2016/2017 as x Then x-25% of x=4.2 x-25x/100=4.2 Using L.C.M 100x-25x/100 =4.2 Cross Multiply 100x-25x=4.2*100 75x=420 x=420/75 x=5.6 Therefore,the bill in 2016/2017 was £5.6 million.
 Sweatballs
Medicmind Tutor
Sweatballs
Medicmind Tutor
Mon, 06 Jun 2022 15:34:03
how is the change since 18/19 to 17/18- -1.2?! Surely it would be 3-1.2? Because in 17/18 they got 1.2 less, not -(-)?! If they got 1.2 less than the 18/19 they'd have got 1.8mil that year for coaching
 Maariyah
Medicmind Tutor
Maariyah
Medicmind Tutor
Wed, 17 Aug 2022 14:33:29
The change from the previous year was that 1.2 had been minused. To figure out what it was the previous year, add the 1.2 back on: 3+1.2=4.2
The budget for the Hornets, a premiership rugby club.

Explanation
Answer: B
Explanation:
1. Find the proportion of the budget spent on all types of staff:
Proportion on staffing = Staffing costs / Total budget:
Staffing cost:
8.5 + 3 + 1.5 + 0.275 = 13.275 million
Total budget = 17.9125 million
13.275/17.9125 = 0.7411 = 74.1%
Top Tip: Remember that proportions compare a single value in comparison to the total. Here, the value is £13.275 million in comparison to the total of £17.9125 million
The budget for the Hornets, a premiership rugby club.

Explanation
Answer: B
Explanation:
1. Find the amount spent on marquee players and non-marquee players:
1.2.+ 12.7% of 8.5 million = £2.2795 million
8.5 – 2.1271 = £6.2205 million
2. Set up a ratio for the marquee players to non-marquee players:
2.2795: 6.2205
3. Simplify this ratio:
We know that one side is equal to one so divide through by 2.2795 as it must be the highest common factor:
6.2205/2.2795 = 2.73 = 3
Therefore, the simplified ratio is 1:3
 Sami
Medicmind Tutor
Sami
Medicmind Tutor
Sat, 31 Jul 2021 18:44:53
Why add 1.2
 k
Medicmind Tutor
k
Medicmind Tutor
Wed, 15 Sep 2021 13:17:44
@Sami, 'all of the playing staff wage increase was due to the signing of a new marquee player'. the 1.2mil increase from 2017/18 to 2018/19 is solely based on the new marquee. Hence to find the amount spent on marquee players u add this and the 2nd marquee player's wage
 Ro
Medicmind Tutor
Ro
Medicmind Tutor
Thu, 22 Sep 2022 23:21:53
In step 1: there is a mistake the line should read - 8.5 - 2.2795 not 8.5 - 2.1271 as the former is 6.2205 and the latter is not that number. Can this be changed?
 ST
Medicmind Tutor
ST
Medicmind Tutor
Sun, 09 Apr 2023 12:49:38
The Q says the marquee player salaries do not count towards the league’s salary cap. In which case their combined salaries are not taken from the players’ salaries of 8.5. The ratio is then 2.2795 (combined marquee salaries) : 8.5 (player salaries minus the marquee players) = 3.72 = approx 1:4
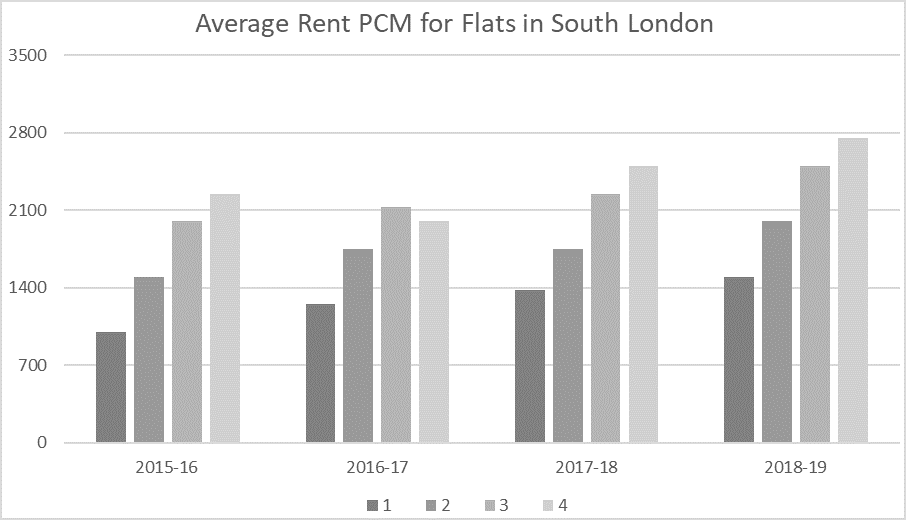
This graph shows the average rent per calendar month (PCM) in a popular area of South London.
A year is made up of 12 calendar months.
Explanation
Answer: B
Explanation:
1. Work out his rent in each of the years.
He paid 75% of the market average (which was £1000 PCM).
0.75 x 1000 = 750
The average price increased from 1000 to 1250.
To find the percentage increase use the formula:
New Value / Old Value = Multiplier
1250/1000 = 1.25 = 25%
His rent increased at double this rate so 50%.
For a percentage increase:
New value = Old value x multiplier
50% increase = multiplier of 1.5
New rent = 750 x 1.5
New rent = £1125
2. Find the difference from the market rent
The graph shows that the new average rent is £1250.
£1250 – £1125 = £125 so he pays £125 below the market rate.
Top Tip: Look over the Multiplier Method lesson on the Online Portal – getting to grips with it will save you time.
 hannah
Medicmind Tutor
hannah
Medicmind Tutor
Thu, 24 Jun 2021 18:40:51
How is the market average £1000 in 2015?
 zena
Medicmind Tutor
zena
Medicmind Tutor
Sun, 22 Aug 2021 16:40:57
How is it 1000pounds in 2015?
 k
Medicmind Tutor
k
Medicmind Tutor
Wed, 15 Sep 2021 13:30:38
@hannah @zena, I believe its the average rent for the first quarter of 2015
 Craig
Medicmind Tutor
Craig
Medicmind Tutor
Wed, 20 Jul 2022 18:14:28
The hardest part of this question is interpreting a graph at increments of 700. The 1000 pcm is not clear.
 Jay
Medicmind Tutor
Jay
Medicmind Tutor
Mon, 25 Jul 2022 15:17:48
I didn't like this Q. The market average for 2015 as a whole is not the same as for the 1st quarter.
 Fi
Medicmind Tutor
Fi
Medicmind Tutor
Mon, 08 Aug 2022 10:59:06
I cannot accurately read these bs graphs
 cum
Medicmind Tutor
cum
Medicmind Tutor
Sun, 14 Aug 2022 18:14:27
agreed
 Alex
Medicmind Tutor
Alex
Medicmind Tutor
Wed, 21 Sep 2022 13:47:57
The key represents the number of beds in the flat. Harry is renting a 1 bed in 2015-16 so you only have to read the darkest bar.
This graph shows the average rent per calendar month (PCM) in a popular area of South London.
A year is made up of 12 calendar months.

Explanation
Answer: B
Explanation:
1. Work out the price he charges each tenant and so the income
The first tenants, he charges at the rate for 2015-16 – £2000 PCM
He does this for 24 months so: 2000 x 24 = £48,000
The second tenants, he charges at the new average rate for 2017-18 – £2250
Again, he does this for 24 months: 2250 x 24 = £54,000
54,000 + 48,000 = £102,000 – B.
Timing Tip: When adding numbers in the thousands, remember that you don’t have to write out every digit. 54 + 48 = 102 and is easier to do as mental maths or on the whiteboard.
 kn
Medicmind Tutor
kn
Medicmind Tutor
Wed, 15 Sep 2021 13:37:07
why is it that the rate for 2015-16 is 2000? Isn't the average for the beginning of 15 1000?
 R
Medicmind Tutor
R
Medicmind Tutor
Thu, 07 Oct 2021 13:30:10
@kn it is a 3 bedroom apartment so you look at the third bar which goes to 1000
 R
Medicmind Tutor
R
Medicmind Tutor
Thu, 07 Oct 2021 13:30:33
2000*
 Anon
Medicmind Tutor
Anon
Medicmind Tutor
Fri, 09 Jun 2023 03:36:47
The math itself is basic. Is there a better way to read the graph than just guesstimating? Or is there a way to guesstimate more accurately??
This graph shows the average rent per calendar month (PCM) in a popular area of South London.
A year is made up of 12 calendar months.

Explanation
Answer: C
Explanation:
1. Find the new rent
The initial rent was double the average market rate in 2017-18.
2500 x 2 = 5000.
He now charges 60% of that:
0.6 x 5000 = £3000.
2. Find the RTV
RTV = Monthly Rental Income / Property Value
RTV = 3000 / 600,000
RTV = 0.005 = 0.5% – option C.
Common Trap: Watch out when there are values which are different by a factor of 10 – it could be a sign that there is a common conversion error.
This graph shows the average rent per calendar month (PCM) in a popular area of South London.
A year is made up of 12 calendar months.

Explanation
Answer: C
Explanation:
1. Find the monthly rent of each and answer by inspection:
In both years, she was paying half the rent.
The rent in 2015-16 for a two-bedroom was £1500 PCM – the same as for a
one-bedroom flat in 2018-19 so, with no further calculation, we can say she paid the same in both years.
Top Tip: Identifying questions which can be answered by inspection will save precious time by avoiding completely unnecessary calculations.
 H
Medicmind Tutor
H
Medicmind Tutor
Thu, 01 Jul 2021 01:52:08
The question didn't state that she paid for half the rent when she was living with her friend. Although the answer is reasonable, it doesn't follow the context of the question- even though it makes sense, we can't assume that she paid for half the rent when living with her friend. She could have paid more or less.
 E
Medicmind Tutor
E
Medicmind Tutor
Mon, 02 Aug 2021 19:11:33
The question is worded as if she only pays half when living with her partner
 L
Medicmind Tutor
L
Medicmind Tutor
Sat, 04 Sep 2021 21:53:36
Hi,how can we assume that she paid half when living with her friend
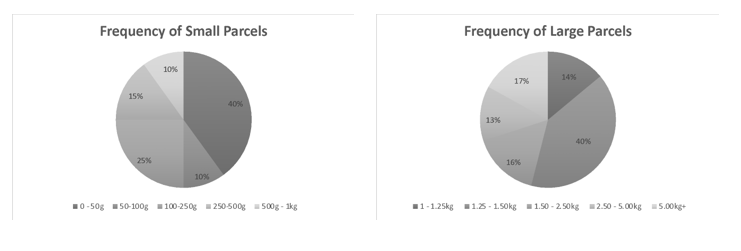
A village Post Office offers small parcel and large parcel delivery. Letters are classed as small parcels.
In the month of January, the same total number of small and large parcels were paid for and posted. The frequency of each is provided in the pie charts.
The pricing for large parcels is given in the table below:
|
Size
|
Price for Standard Delivery ($) |
Price for Recorded Delivery ($) |
|
1 – 1.25 |
7.25 |
14.25 |
|
1.25 – 1.5 |
8.25 |
15.50 |
|
1.5 – 2.5 |
9.50 |
17.00 |
|
2.5 – 5 |
10 |
18.50 |
|
5+ |
12.50 + 0.10 per additional 100g above 5 kg |
20.00 + 0.12 per additional 100g above 5kg |
Explanation
Answer: C
Explanation:
1. Find the percentage increase.
A percentage increase can be found using the formula:
![]()
He initially would have gone for a 1.45kg package (in the 1.25-1.5kg band) at standard delivery – $8.25.
He is now going for a 1.55kg package (in the 1.5-2.5kg band) with recorded delivery ($17.00)
![]()
This means that the percentage increase is 106%.
Top Tip: It is worth spending the time getting used to the multiplier method. Our research shows that it does save time
A village Post Office offers small parcel and large parcel delivery. Letters are classed as small parcels.
In the month of January, the same total number of small and large parcels were paid for and posted. The frequency of each is provided in the pie charts.

The pricing for large parcels is given in the table below:
|
Size
|
Price for Standard Delivery ($) |
Price for Recorded Delivery ($) |
|
1 – 1.25 |
7.25 |
14.25 |
|
1.25 – 1.5 |
8.25 |
15.50 |
|
1.5 – 2.5 |
9.50 |
17.00 |
|
2.5 – 5 |
10 |
18.50 |
|
5+ |
12.50 + 0.10 per additional 100g above 5 kg |
20.00 + 0.12 per additional 100g above 5kg |
Explanation
Answer: B
Explanation:
1. Find the percentage of parcels below 1.25kg.
The question information states that there were an equal number of small and large parcels. All of the small parcels (50% of the total) were less than 1.25kg.
From the large parcels – 14% were 1 – 1.25kg. This means that 14% of the 50% that were large were less than 1.25kg.
This can be calculated using decimals:
50% of 14% = 7%
The total which are less than 1.25kg is therefore:
50% + 7% = 57%.
Common Trap: It is important to see that the 14% of parcels between 1 – 1.25kg represent 14% of the 50% that are large parcels. Therefore, it only represents 7% of the total of parcels.
A village Post Office offers small parcel and large parcel delivery. Letters are classed as small parcels.
In the month of January, the same total number of small and large parcels were paid for and posted. The frequency of each is provided in the pie charts.

The pricing for large parcels is given in the table below:
|
Size
|
Price for Standard Delivery ($) |
Price for Recorded Delivery ($) |
|
1 – 1.25 |
7.25 |
14.25 |
|
1.25 – 1.5 |
8.25 |
15.50 |
|
1.5 – 2.5 |
9.50 |
17.00 |
|
2.5 – 5 |
10 |
18.50 |
|
5+ |
12.50 + 0.10 per additional 100g above 5 kg |
20.00 + 0.12 per additional 100g above 5kg |
Explanation
Answer: D
Explanation:
1. Find the new prices for each:
The new price can be found using the formula:
NewValue=OldValue×Multiplier
The percentage increase of 38% gives a multiplier 1.38:
For the standard postage:
9.50 x 1.38 = $13.11
For the recorded postage:
17.00 x 1.38 = $23.46
2. Find the difference for the old and the new prices
Old: 17.00 – 9.50 = $7.50
New: 23.46 – 13.11 = $10.35
Difference: 10.35 – 7.50 = $2.85 – option D
 R
Medicmind Tutor
R
Medicmind Tutor
Thu, 07 Oct 2021 13:43:47
Im so disappointed i did 17-9.5 as 8.5 in my head straight away without any second thought ????
 orange
Medicmind Tutor
orange
Medicmind Tutor
Thu, 11 Aug 2022 10:37:43
'increasing by the same amount' implies that it increases by x pounds . A more suited phrase would be that it 'increased by the same percentage'.
A village Post Office offers small parcel and large parcel delivery. Letters are classed as small parcels.
In the month of January, the same total number of small and large parcels were paid for and posted. The frequency of each is provided in the pie charts.

The pricing for large parcels is given in the table below:
|
Size
|
Price for Standard Delivery ($) |
Price for Recorded Delivery ($) |
|
1 – 1.25 |
7.25 |
14.25 |
|
1.25 – 1.5 |
8.25 |
15.50 |
|
1.5 – 2.5 |
9.50 |
17.00 |
|
2.5 – 5 |
10 |
18.50 |
|
5+ |
12.50 + 0.10 per additional 100g above 5 kg |
20.00 + 0.12 per additional 100g above 5kg |
Explanation
Answer: B
Explanation:
1. Find the number of parcels sold in the 1 – 1.25kg range.
X is the number of parcels sold which were in the 1 – 1.25kg range.
They sold 0.5X of these recorded.
They sold 0.5X of these standard.
752.50 = 0.5X x 14.25 + 0.5X x 7.25
752.50 = 10.75X
X = 752.50 / 10.75
X = 70 – this is 14% of the number of large parcels
2. Find the number in the range 500g – 1kg.
Let us call the total number of large parcels Y:
14% of Y = 70
0.14Y = 70
Y = 70/0.14
Y = 500
The question information states that there are an equal number of large and small parcels.
Therefore, there are 500 small parcels. 10% of small parcels are 500g – 1 kg.
1. x 500 = 50 – B
Common Trap: This question relied on noticing that the number of large parcels is equal to the number of small parcels. Always read the bullet points below tables in the scenario.
 maira
Medicmind Tutor
maira
Medicmind Tutor
Thu, 29 Jul 2021 11:22:59
how do we get 10.75x
 L
Medicmind Tutor
L
Medicmind Tutor
Sat, 04 Sep 2021 23:52:10
Hi there, how do you know that 70 =14 percent of the no. of large parcels?
 R
Medicmind Tutor
R
Medicmind Tutor
Thu, 07 Oct 2021 14:00:55
How did you know that the number of small parcels and large parcels are equal. The common trap says to notice the bullet points. The bullet point states that in JANUARY the number of small and large parcels were equal, not december. We cannot assume that the number of large and small parcels are equal for every month. The wording of these questions are so misleading.
 ST
Medicmind Tutor
ST
Medicmind Tutor
Sun, 09 Apr 2023 16:20:02
R is right in that the bullet points are relevant to January sales; the Q is asking about December sales, for which we have no information. The ‘correct’ answer should then be ‘Cannot Tell’. This isn’t offered. So then, assuming the December & January frequency data is the same… We don’t know how many parcels are in the 1-1.25kg range. So we substitute ‘x’ for that number. We do, however, know the full cost of the sales of these parcels: $752.50. We know 50% of x parcels were sent standard delivery (SD) at $7.25/parcel. We know 50% of x parcels were send recorded delivery (RD) at $14.25/parcel. Thus $752.50 = (0.5x * 7.25) + (0.5x * 14.25) $752.50 = 3.125x + 7.125x $752.50 = 10.25x 752.50 / 10.25 = 70 Thus there were 70 parcels in the 1-1.25kg range. If you look at the frequency data in the pie charts… The parcels in the 1-1.25kg range were 14% of the total parcels (small + large). 70 / 14 = 1% of the parcels = 5 parcels. 10% of total parcels were in the 500-1kg range. Thus, if 1% = 5 parcels, 5 x 10 = 10% of total parcels = 50 parcels.
Explanation
Answer: B
Explanation:
1. Find the first discount.
It is a 40% discount, so the new price is 0.6 times the full price.
2 Find the second discount.
It is a 10% discount so the price for paying upfront is 0.9 times the discounted price.
0.9 x 0.6 = 0.54 – 54%.
This means that the answer is B
Common trap: Note that the 10% discount is on the new price. This means the calculation is 0.6 x 0.9 rather than 0.6 – 0.1 = 0.5 or 50% discount.
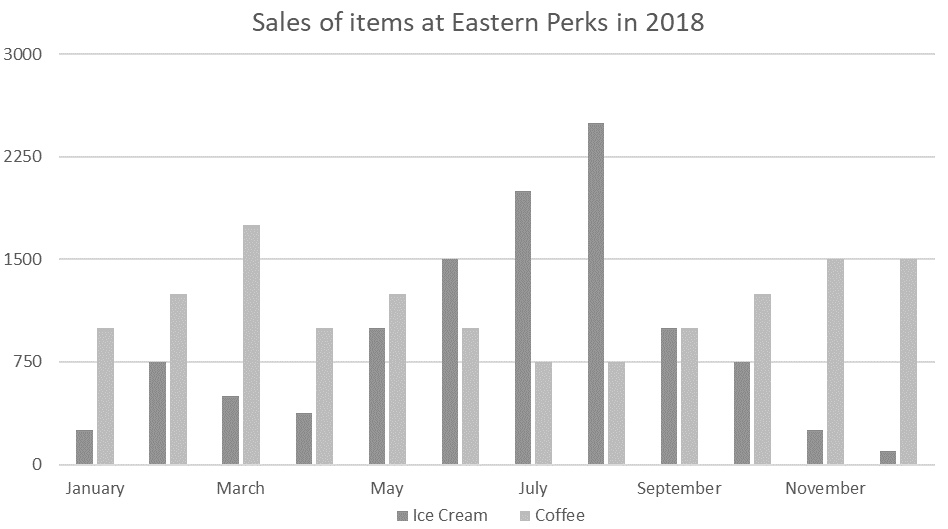
- Eastern Perks is a café selling coffee and ice cream.
- The graph shows the number of each product sold in each month of the year.
- Their year is split into four quarters: Q1: January to March, Q2: April to June, Q3: July to September and Q4: October to December.
- The cafe offers a rewards card where customers’ 7th coffee is free. They offer the opportunity to “pay this forward” where the customer donates it to the Eastern Perks Foundation which provides free coffee to those on the margins of society.
Explanation
Answer: D
Explanation: The question has asked for the June value as a percentage of the May value.
1. Find the May and June values:
June: From the graph, this is roughly 1500.
May: From the graph, this is roughly 1000.
2. Find 1500 as a percentage of 1000.
New value / Old value = Multiplier.
1500/1000 = 1.5 = 150%.
Common Trap: Notice this has asked for the June value as a percentage of May rather than asking for the percentage increase.
 Roha Alam
Medicmind Tutor
Roha Alam
Medicmind Tutor
Fri, 25 Sep 2020 16:16:11
the graph doesnt load

- Eastern Perks is a café selling coffee and ice cream.
- The graph shows the number of each product sold in each month of the year.
- Their year is split into four quarters: Q1: January to March, Q2: April to June, Q3: July to September and Q4: October to December.
- The cafe offers a rewards card where customers’ 7th coffee is free. They offer the opportunity to “pay this forward” where the customer donates it to the Eastern Perks Foundation which provides free coffee to those on the margins of society.
Explanation
Answer: B
Explanation:
1. Find the average for each for the first quarter.
For many questions, this could be done by estimation through eyeballing the graphs to save time. However, this one has a scale which has too wide a margin of error for this.
For Coffee: (1000 + 1250 + 1750) / 3 = 4000/3
For Ice cream: (250 + 500 + 750) / 3 = 500
2. Find the average for each for the final quarter:
For Coffee: (1250 + 1500 + 1500) / 3 = 4250/3
For Ice cream: (750 + 250 + 100) / 3 = 1100/3
3. Find the difference in averages:
C: 4250/3 – 4000/3 = 83.3
I: 500 – 1100/3 = 133.3
133.3 – 83.3 = 50.
Timing Tip: Some QR questions would take longer than 40s to answer. Try to identify these and learn to be disciplined so that you are not spending 120s making sure that you get the answer right.

- Eastern Perks is a café selling coffee and ice cream.
- The graph shows the number of each product sold in each month of the year.
- Their year is split into four quarters: Q1: January to March, Q2: April to June, Q3: July to September and Q4: October to December.
- The cafe offers a rewards card where customers’ 7th coffee is free. They offer the opportunity to “pay this forward” where the customer donates it to the Eastern Perks Foundation which provides free coffee to those on the margins of society.
Explanation
Answer: D
Explanation:
1. Find the number of each type of ice cream sold:
1500 + 2000 = 3500 ice creams.
2/5ths are large so 0.4 x 3500 = 1400
3/5ths are small so 0.6 x 3500 = 2100
Top tip: This method is known as calculation by proportions – these come up in Lesson 6.
2. Find the revenue from each type of ice cream and thus the difference:
The large ice creams are £2.75:
1400 x 2.75 = £3850
The small ice creams are £2:
2100 x 2 = £4100
Find the difference between the two:
4100 – 3850 = £350
 k
Medicmind Tutor
k
Medicmind Tutor
Wed, 06 Apr 2022 08:32:48
your answer is correct, but you have made a mistake in working out. It should be 4200 for price of small ice-cream not 4100 as 2100x2=4200

- Eastern Perks is a café selling coffee and ice cream.
- The graph shows the number of each product sold in each month of the year.
- Their year is split into four quarters: Q1: January to March, Q2: April to June, Q3: July to September and Q4: October to December.
- The cafe offers a rewards card where customers’ 7th coffee is free. They offer the opportunity to “pay this forward” where the customer donates it to the Eastern Perks Foundation which provides free coffee to those on the margins of society.
Explanation
Answer: B
Explanation:
1. Find the approximate coffee sales in the first quarter in 2018 and therefore the 2019 target.
1000+1250+1750 = 4000
The manager wants 5% growth.
4000 x 1.05 = 4200
2. Find the sales in January and February.
In 2018: 1000 + 1250 = 2250
In 2019: 2250 x 1.02 = 2295
3. Find the necessary number for March:
The cafe need to meet the target of 4200 so:
4200 – 2295 = 1905.
Top Tip: Graphs often have far more information than will be required to answer the question. Here, focus on the three bars which represent coffee sales in the first quarter.
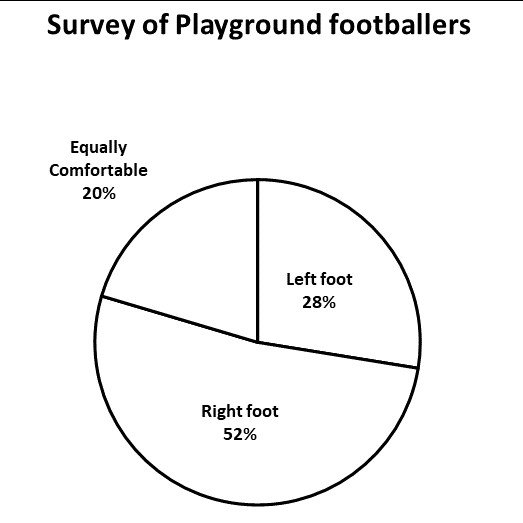
● This survey shows the preferred foot of a number of playground footballers.
● They were also asked about what hand they write with.
● There were no ambidextrous individuals in the group (i.e. those that could use both hands to write).
Explanation
Answer: B
Explanation:
1. Find the number of each group who are left handed.
⅚ of the left-footed people are left-handed:
5/6 x 54 = 45
16.7% of the right-footed people are left-handed:
0.167 x 102 = 17
90% of those who expressed no preference are left-handed:
0.9 x 40 = 36
This means that the total is:
45+17+36 = 98
2. Find the total interviewed and thus the percentage who are right-handed:
40+54+102 = 196
If 98 are left handed:
196 – 98 = 98 right handed people
98/196 = 50%
 Dan
Medicmind Tutor
Dan
Medicmind Tutor
Sun, 30 Aug 2020 15:59:02
"5/6 of the left-footed people are left-handed - 5/6 x 54 = 45. Could you please explain where the 54 is coming from.
 lin
Medicmind Tutor
lin
Medicmind Tutor
Tue, 08 Sep 2020 16:16:55
where does the 54, 102 and 40 come from?
 jiys
Medicmind Tutor
jiys
Medicmind Tutor
Sat, 24 Jul 2021 12:57:58
how do you find total interviewed
 Moira
Medicmind Tutor
Moira
Medicmind Tutor
Thu, 19 Aug 2021 06:00:15
The more I do your tests, the more I am confused. You do not fully explain where some numbers come from. In this example, where did you get the 54, 102, from?? you explanation lack logic. Thanks
 L
Medicmind Tutor
L
Medicmind Tutor
Sun, 05 Sep 2021 00:32:17
I think the answer can be worked out by imaging the total is 100 therefore 5/6 of 28 people and so on
 Laisa
Medicmind Tutor
Laisa
Medicmind Tutor
Mon, 06 Sep 2021 16:52:49
Am I blind or am I fully missing where the 54, 102 and 40 came from?
 Winner
Medicmind Tutor
Winner
Medicmind Tutor
Sat, 22 Jan 2022 09:24:49
There is no total nbr of player indicated
 Andre
Medicmind Tutor
Andre
Medicmind Tutor
Thu, 02 Jun 2022 05:49:04
We still haven’t found out where the 54 102 and 40 come from?
 UCAT GOAT
Medicmind Tutor
UCAT GOAT
Medicmind Tutor
Wed, 20 Jul 2022 18:14:58
The numbers 54,102 and 40 come from extrapolating values. The method shown is therefore incorrect. This is a question you should definitely skip in the exam
 Alex
Medicmind Tutor
Alex
Medicmind Tutor
Wed, 21 Sep 2022 14:29:20
Assume total number of players surveyed is 100. (This now means 28% of players = 28 players exactly) 1) 100*(5/6)= 83.3% therefore 0.833 x 28 = 23 LF+LH players 2) 0.167 x 52 = 8.684 = 9 RF+LH 3) 0.90 x 20 = 18 EQ+LH 23 + 9 + 18 = 50 players who are left handed As we have assumed there are 100 players 100 - 50LH = 50 RH players which = 50% RH
Explanation
Answer: A
Explanation:
Top tip: The best method is to use a value of 100 individuals – this allows easy calculations from percentages.
1. Draw a Venn Diagram to represent the situation.
A + B + C + 30 = 100
A + B + C = 70
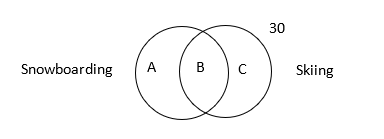
2. Form equations for the number who can do each of the activities and solve to find C then B.
Snowboarding: A + B = 43
Skiing: B + C = 34
Substitute the equation for snowboarding into the first equation to find the
value of C.
A + B + C + 30 = 100
A + B = 43
43 + C + 30 = 100
C = 27
Thus find the value of B
We know from the skiing group that:
B + C = 34
B + 27 = 34
B = 7% – A.
 huh
Medicmind Tutor
huh
Medicmind Tutor
Sat, 14 Aug 2021 18:01:41
it says 30 could not do both not neither
 Moira
Medicmind Tutor
Moira
Medicmind Tutor
Thu, 19 Aug 2021 06:09:41
Extremely confusing! A + B + C + 30 = 100 Here, A snowB 43%, B Ski 34% and C None 30% = 107! unlike above, Really MedicMind, you need more clarity in your explanation and fully show how to you get these results.
 UCAT GOAT
Medicmind Tutor
UCAT GOAT
Medicmind Tutor
Wed, 20 Jul 2022 18:17:52
We know we need 100% total in the diagram. We can remove 30 as these are not involved whatsoever. Therefore, we'd expect a value of 70, which we do not have, instead we have 77, therefore 7% must be shared between the two groups.
|
Revenue Stream |
January Revenue (000s) |
February Revenue (000s) |
March Revenue (000s) |
|
Teaching |
120 |
145 |
130 |
|
Mentoring |
15 |
17.5 |
19 |
|
Writing |
80 |
90 |
101 |
- This is the revenue for a medium-to-large-sized business in Australia.
- All figures are given in AUD$
Explanation
Answer: B
Explanation:
1. Find the sum of the incomes and find the monthly average:
(120 + 145 + 130 + 15 +17.5 19 + 80 + 90 + 101) x 1000 = $717,500
Divide this by 3 to find the monthly average.
$717,500/3 = $239,166… = $239,250 to the nearest $250.
Common Trap: Remember that the question is looking for the average monthly income rather than the mean income from each revenue stream.
|
Revenue Stream |
January Revenue (000s) |
February Revenue (000s) |
March Revenue (000s) |
|
Teaching |
120 |
145 |
130 |
|
Mentoring |
15 |
17.5 |
19 |
|
Writing |
80 |
90 |
101 |
- This is the revenue for a medium-to-large-sized business in Australia.
- All figures are given in AUD$
Explanation
Answer: B
Explanation:
1. Find the multiplier:
130/145 = 0.89655… = 10.345 % percentage decrease
To the nearest 0.1%, this is 10.3%
Top tip: The answer options are 0.1% away so it will be necessary to work precisely.
Top tip: The multiplier method will save time – get to grips with it in practice and you will save precious seconds.
 Moira
Medicmind Tutor
Moira
Medicmind Tutor
Thu, 19 Aug 2021 07:41:30
I do not get the answer! where the 10.345 come from. I tried to get the calculation right but I think I am missing something here. Thanks
 Sab
Medicmind Tutor
Sab
Medicmind Tutor
Mon, 26 Sep 2022 03:26:54
How do you get from 0.896 to 10.3% ?
 ST
Medicmind Tutor
ST
Medicmind Tutor
Mon, 10 Apr 2023 07:53:21
145-130 = 15. This is the difference between Feb & March. 15 / 145 = 0.1034. This is 10.34% decrease from Feb to March. 10.3 to the nearest 0.1%.
|
Revenue Stream |
January Revenue (000s) |
February Revenue (000s) |
March Revenue (000s) |
|
Teaching |
120 |
145 |
130 |
|
Mentoring |
15 |
17.5 |
19 |
|
Writing |
80 |
90 |
101 |
- This is the revenue for a medium-to-large-sized business in Australia.
- All figures are given in AUD$
Explanation
Answer: C
Explanation:
1. Find the total income from teaching:
120 + 145 + 130 = 395
2. Find the February revenue as a proportion of that:
145/395 = 0.367… = 37% to the nearest percentage point
Top tip: Proportion is the comparison of one characteristic with the whole group.
|
Revenue Stream |
January Revenue (000s) | February Revenue (000s) |
March Revenue (000s) |
| Teaching | 120 | 145 | 130 |
| Mentoring | 15 | 17.5 | 19 |
| Writing | 80 | 90 | 101 |
- This is the revenue for a medium-to-large-sized business in Australia.
- All figures are given in AUD$
Explanation
Answer: D
Explanation:
1. Find the profit for each:
Teaching: 0.4 x 130,000 = $52,000
Writing: 0.52 x 101,000 = $52,520
2. Find the percentage difference between the two:
52,520/52000 = 1.01
Therefore, writing has a higher profit by 1%.
Common trap: The profit margin is different by 12% but this is not the same as the profit being different by 12%. The profit is also dependent on the level of revenue which is very different for the two revenue streams.
 Maria
Medicmind Tutor
Maria
Medicmind Tutor
Sun, 07 Mar 2021 18:49:59
The wrong answer has been selected.
 Husna Abedi
Medicmind Tutor
Husna Abedi
Medicmind Tutor
Mon, 26 Jul 2021 15:10:09
This explanation is very confusing as it doesn't match the answer options
 leah
Medicmind Tutor
leah
Medicmind Tutor
Thu, 21 Jul 2022 10:22:42
how i got the answer was i found 40% of teaching and 52% of writing and i took away the highest number which was writing 52,52 away from teaching which was 52 and got 0.52 but always round it up so 0.5%
 ST
Medicmind Tutor
ST
Medicmind Tutor
Mon, 10 Apr 2023 08:08:21
?? The answer ‘explanation’ does not match the responses available. 40% of 130 = 52. 52% of 101 = 52.52. (All in multiples of 1000 so why bother including the 1000s?) To find the percentage difference between these two values… 52.52 / 52 = 1.01. 0.01 = 1%. 52.52 is therefore 1% larger than 52. 0.52 is the difference in AUD$ between the absolute values of the profits from both items. 1% is the percentage difference between the profits from both items. ?
 Anon
Medicmind Tutor
Anon
Medicmind Tutor
Fri, 09 Jun 2023 03:53:21
@leah Subtracting 52 from 52.52 gets the actual value difference in profit, not the percentage difference. I think the MCQ answer itself is wrong - there should be 1% difference instead of 0.5%
Percentages & Proportion Review Screen
Instructions
Below is a summary of your answers. You can review your questions in three (3) different ways.
The buttons in the lower right-hand corner correspond to these choices:
1. Review all of your questions and answers.
2. Review questions that are incomplete.
3. Review questions that are flagged for review. (Click the 'flag' icon to change the flag for review status.)
You may also click on a question number to link directly to its location in the exam.
Percentages & Proportion Section
Final Answer Review Screen
Instructions
This review section allows you to view the answers you made and see whether they were correct or not. Each question accessed from this screen has an 'Explain Answer' button in the top left hand side. By clicking on this you will obtain an explanation as to the correct answer.
At the bottom of this screen you can choose to 'Review All' answers, 'Review Incorrect' answers or 'Review Flagged' answers. Alternatively you can go to specific questions by opening up any of the sub-tests below.
Percentages & Proportion Section
TI-108