Your Time has Finished
Loading...
GAMSAT Section III Biology Questions Part 2
Your Score: %
Average Score of All Users:
You performed better than of students
Section Breakdown
| Your Score | Average of all Users | Percentile | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biology Questions Part 2 |
Biology Questions Part 2
Your score:
Average score:
You performed better than of students
Speed as well as accuracy is important in this section. Work quickly, or you might not finish the paper. There are no penalties for incorrect responses, only marks for correct answers, so you should attempt all questions. Each question is worth one mark.
You must complete the answers within the time limit. Calculators are NOT permitted.
Good Luck!
Biology: body systems
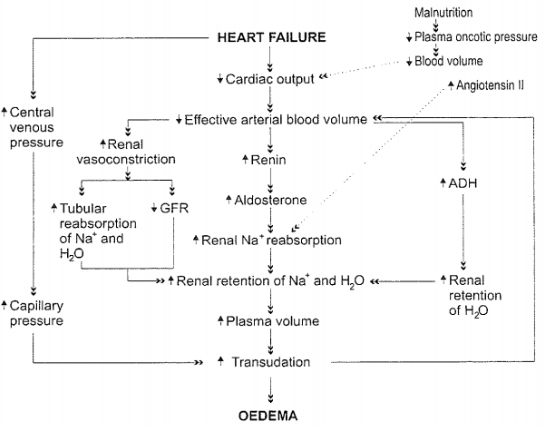
Oedema is an excessive accumulation of fluid in tissue spaces or a body cavity. It can have many harmful effects, for example impaired healing.
The diagram below indicates the events that lead to systemic oedema in heart failure.
The following points may also be of use:
- Increasing plasma volume increases blood pressure
- Transudation is the passing of fluid through pores
- ADH is antidiuretic hormone
- GFR is glomerular filtration rate
Explanation
The correct answer is C.
Diagram indicates that transudation causes a decrease in arterial blood volume, which leads to repetition of renin-aldosterone pathway, which would augment the transudation and oedema.
Biology: body systems
Oedema is an excessive accumulation of fluid in tissue spaces or a body cavity. It can have many harmful effects, for example impaired healing.
The diagram below indicates the events that lead to systemic oedema in heart failure.
The following points may also be of use:
- Increasing plasma volume increases blood pressure
- Transudation is the passing of fluid through pores
- ADH is antidiuretic hormone
- GFR is glomerular filtration rate

Explanation
The correct answer is D.
Tubular reabsorption (not excretion) leads to renal retention of sodium. Also renal retention of sodium contributes to an increase in plasma volume.
Biology: body systems
Oedema is an excessive accumulation of fluid in tissue spaces or a body cavity. It can have many harmful effects, for example impaired healing.
The diagram below indicates the events that lead to systemic oedema in heart failure.
The following points may also be of use:
- Increasing plasma volume increases blood pressure
- Transudation is the passing of fluid through pores
- ADH is antidiuretic hormone
- GFR is glomerular filtration rate

Explanation
The correct answer is A.
Increase in Angiotensin II ???? increased renal sodium reabsorption ???? increase in plasma volume ???? increase in blood pressure.
Biology: body systems
Oedema is an excessive accumulation of fluid in tissue spaces or a body cavity. It can have many harmful effects, for example impaired healing.
The diagram below indicates the events that lead to systemic oedema in heart failure.
The following points may also be of use:
- Increasing plasma volume increases blood pressure
- Transudation is the passing of fluid through pores
- ADH is antidiuretic hormone
- GFR is glomerular filtration rate

Explanation
The correct answer is D.
ADH causes a retention in water, not sodium (as per the diagram)
ENDOCRINE
Stress stimulates physiological reactions within the body which are regulated by the endocrine system. The main organ stimulated by stress is the hypothalamus, which initiates immediate responses. These responses can be accompanied by (and are followed by) a stage of stress resistance. The effects of stress on the hypothalamus can be seen in the diagram below.
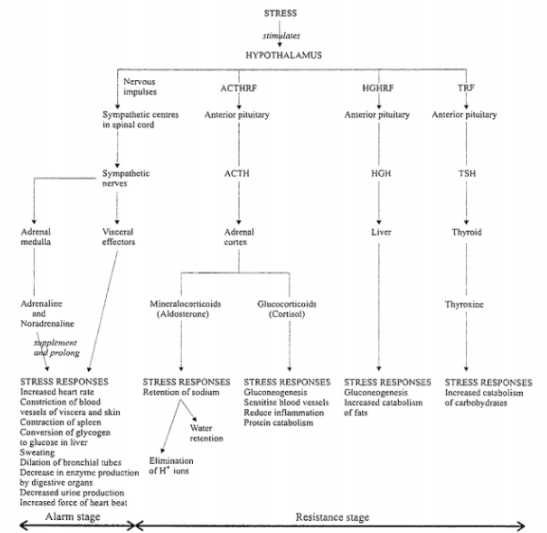
Abbreviation used in the diagram:
ACTHRF: Adrenocorticotrophic hormone releasing factor
HGHRF: Human growth hormone releasing factor
TRF: Thyrotropin releasing factor
ACTH: Adrenocorticotrophic hormone
HGH: Human growth hormone
TSH: Thyroid stimulating hormone
Explanation
The correct answer is B.
The diagram shows that both heart rate and force of heartbeat increase (so circulation increases). There is also a decrease in digestive enzymes (so digestion decreases).
ENDOCRINE
Stress stimulates physiological reactions within the body which are regulated by the endocrine system. The main organ stimulated by stress is the hypothalamus, which initiates immediate responses. These responses can be accompanied by (and are followed by) a stage of stress resistance. The effects of stress on the hypothalamus can be seen in the diagram below.

Abbreviation used in the diagram:
ACTHRF: Adrenocorticotrophic hormone releasing factor
HGHRF: Human growth hormone releasing factor
TRF: Thyrotropin releasing factor
ACTH: Adrenocorticotrophic hormone
HGH: Human growth hormone
TSH: Thyroid stimulating hormone
Explanation
The correct answer is B.
Gluconeogenesis (conversion of glycogen to glucose) is shown to occur as a stress response by the liver, by the production of glucocorticoids but the adrenal cortex, and by the production of adrenaline and noradrenaline by the adrenal medulla.
ENDOCRINE
Stress stimulates physiological reactions within the body which are regulated by the endocrine system. The main organ stimulated by stress is the hypothalamus, which initiates immediate responses. These responses can be accompanied by (and are followed by) a stage of stress resistance. The effects of stress on the hypothalamus can be seen in the diagram below.

Abbreviation used in the diagram:
ACTHRF: Adrenocorticotrophic hormone releasing factor
HGHRF: Human growth hormone releasing factor
TRF: Thyrotropin releasing factor
ACTH: Adrenocorticotrophic hormone
HGH: Human growth hormone
TSH: Thyroid stimulating hormone
Explanation
The correct answer is D.
Removal of H+ ions is a stress response that is ultimately regulated by ACTHRF production.
ENDOCRINE
Stress stimulates physiological reactions within the body which are regulated by the endocrine system. The main organ stimulated by stress is the hypothalamus, which initiates immediate responses. These responses can be accompanied by (and are followed by) a stage of stress resistance. The effects of stress on the hypothalamus can be seen in the diagram below.

Abbreviation used in the diagram:
ACTHRF: Adrenocorticotrophic hormone releasing factor
HGHRF: Human growth hormone releasing factor
TRF: Thyrotropin releasing factor
ACTH: Adrenocorticotrophic hormone
HGH: Human growth hormone
TSH: Thyroid stimulating hormone
Explanation
The correct answer is B.
Cortisol reduces inflammation which reduces the formation of new connective tissue. It also makes blood vessels more sensitive to stimuli which causes constriction and results in an increase in blood pressure.
Unit 1: neuro
We have nerve cells that make up motor and sensory pathways travelling both centrally and peripherally until they reach certain parts of our brain. To try and demonstrate this idea, we have a ‘motor homunculus’ and ‘sensory homunculus’ (figure 1). These aim to represent a ‘neurological map’ which shows the areas and proportions of the human brain dedicated to processing motor or sensory function for different areas of the body.
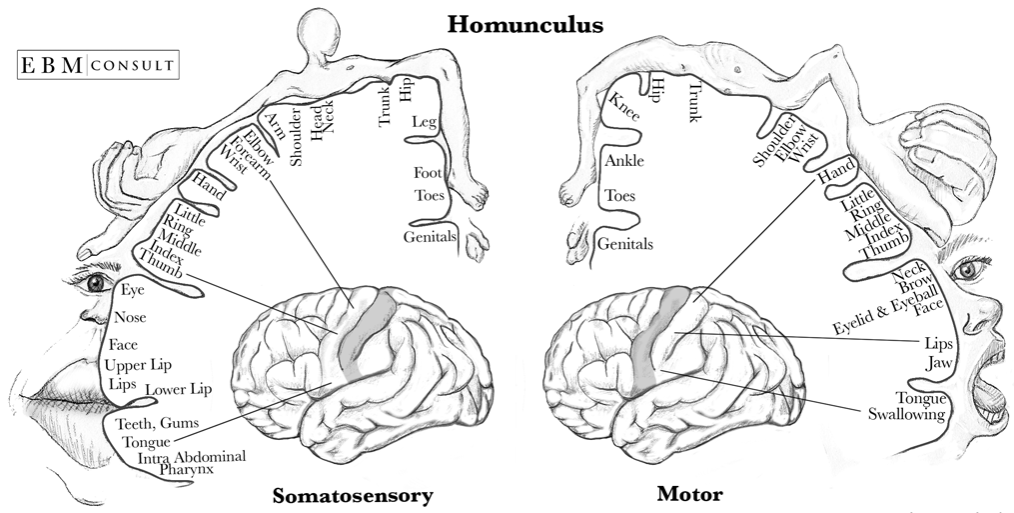
Source: https://www.ebmconsult.com/content/images/Anatomy/Homonculus Sensory and Motor Cortex v2.png
Explanation
The correct answer is C.
In passage ‘area dedicated to processing sensory function’ – this is achieved via receptors.
 Guest
Medicmind Tutor
Guest
Medicmind Tutor
Sun, 08 May 2022 18:49:16
The next questions literally have "pain" in th em, but ok I guess it's part of the passage lol.
 Agne
Medicmind Tutor
Agne
Medicmind Tutor
Tue, 19 Jul 2022 17:27:07
"These aim to represent a ‘neurological map’ which shows the areas and proportions of the human brain dedicated to processing motor or sensory function for different areas of the body", I do believe that this statement suggest that the answer should be A. As no further information is given.
Unit 1: neuro
We have nerve cells that make up motor and sensory pathways travelling both centrally and peripherally until they reach certain parts of our brain. To try and demonstrate this idea, we have a ‘motor homunculus’ and ‘sensory homunculus’ (figure 1). These aim to represent a ‘neurological map’ which shows the areas and proportions of the human brain dedicated to processing motor or sensory function for different areas of the body.

Source: https://www.ebmconsult.com/content/images/Anatomy/Homonculus Sensory and Motor Cortex v2.png
Explanation
The correct answer is A.
Just need to find the largest area represented in sensory diagram.
 Guest
Medicmind Tutor
Guest
Medicmind Tutor
Sun, 08 May 2022 18:48:46
Confusing because I guess lips make up the face, but you tell yourself that they're separate on the diagram
 Ethan
Medicmind Tutor
Ethan
Medicmind Tutor
Sat, 18 Mar 2023 11:31:16
agree! There's literally a "face" label on the diagram
Unit 1: neuro
We have nerve cells that make up motor and sensory pathways travelling both centrally and peripherally until they reach certain parts of our brain. To try and demonstrate this idea, we have a ‘motor homunculus’ and ‘sensory homunculus’ (figure 1). These aim to represent a ‘neurological map’ which shows the areas and proportions of the human brain dedicated to processing motor or sensory function for different areas of the body.

Source: https://www.ebmconsult.com/content/images/Anatomy/Homonculus Sensory and Motor Cortex v2.png
Explanation
The correct answer is C.
Again. Just the biggest.
Unit 1: neuro
We have nerve cells that make up motor and sensory pathways travelling both centrally and peripherally until they reach certain parts of our brain. To try and demonstrate this idea, we have a ‘motor homunculus’ and ‘sensory homunculus’ (figure 1). These aim to represent a ‘neurological map’ which shows the areas and proportions of the human brain dedicated to processing motor or sensory function for different areas of the body.

Source: https://www.ebmconsult.com/content/images/Anatomy/Homonculus Sensory and Motor Cortex v2.png
Explanation
The correct answer is B.
Biggest to smallest.
Unit 2: GI tract
The gastrointestinal system starts at the mouth and ends at the anus (figure 1). Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and waste is expelled as faeces. The upper gastrointestinal tract consists of the mouth, pharynx, oesophagus, stomach, and duodenum. The lower gastrointestinal tract includes most of the small intestine and the large intestine.
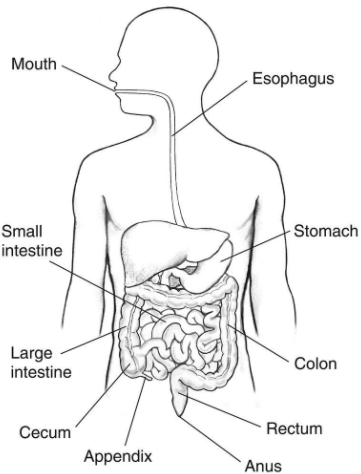
Explanation
The correct answer is A.
Begins with the process of mastication.
Unit 2: GI tract
The gastrointestinal system starts at the mouth and ends at the anus (figure 1). Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and waste is expelled as faeces. The upper gastrointestinal tract consists of the mouth, pharynx, oesophagus, stomach, and duodenum. The lower gastrointestinal tract includes most of the small intestine and the large intestine.

Explanation
The correct answer is A.
B is an immune role and C is peristalsis.
 Agne
Medicmind Tutor
Agne
Medicmind Tutor
Tue, 19 Jul 2022 17:29:25
This is partially incorrect as saliva helps to create bolus, which helps food to slide down the throat into your esophagus. Therefore, there are two correct answers.
 Connor
Medicmind Tutor
Connor
Medicmind Tutor
Mon, 29 Aug 2022 13:44:47
Saliva contains a-amylase which serves as the beginning point of chemical and mechanical digestion.
Unit 2: GI tract
The gastrointestinal system starts at the mouth and ends at the anus (figure 1). Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and waste is expelled as faeces. The upper gastrointestinal tract consists of the mouth, pharynx, oesophagus, stomach, and duodenum. The lower gastrointestinal tract includes most of the small intestine and the large intestine.

Explanation
The correct answer is D.
Seen as a caecal attachment but also least prominent on diagram.
 Mitch
Medicmind Tutor
Mitch
Medicmind Tutor
Fri, 18 Mar 2022 05:24:54
The appendix is part of the large intestine
 Guest
Medicmind Tutor
Guest
Medicmind Tutor
Sun, 08 May 2022 18:51:16
haha
 Connor
Medicmind Tutor
Connor
Medicmind Tutor
Mon, 29 Aug 2022 13:47:27
With respect to the role of digestion, the appendix plays no role whatsoever so D is correct.
Unit 2: GI tract
The gastrointestinal system starts at the mouth and ends at the anus (figure 1). Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and waste is expelled as faeces. The upper gastrointestinal tract consists of the mouth, pharynx, oesophagus, stomach, and duodenum. The lower gastrointestinal tract includes most of the small intestine and the large intestine.

Explanation
The correct answer is D.
It then passes useless waste material from the body. Is the broadest organ and much straighter than small intestine.
Cell biology – cell division
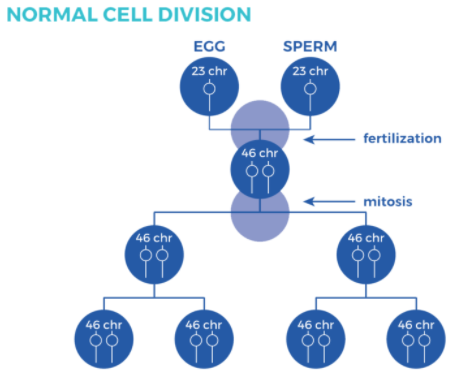
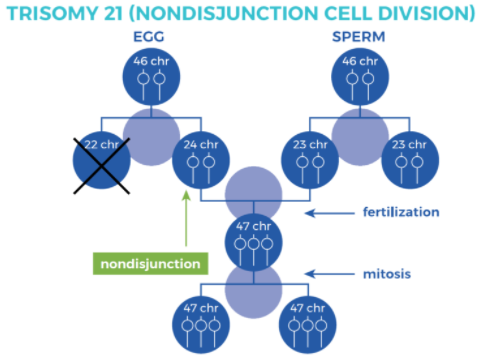
Images reference: https://cmdss.org/parent-guide/about-down-syndrome/types-syndrome/
Above are two diagrams of cell division, one shows normal cell division, and another shows a cell division pathway that results in Down Syndrome.
The stages of mitosis are written below in the wrong order:
• Interphase: the cell grows, performs routine life processes and prepares to divide.
• Cytokinesis: the cytoplasm splits in two and two cells are formed.
• Telophase: Spindle fibres breakdown, nuclear membrane forms and chromosomes begin to uncoil and form chromatin.
• Anaphase: Sister chromatids are pulled apart and move to the opposite poles of the cells.
• Metaphase: Sister chromatids line up at the centre of the cell.
• Prophase: chromosomes are visible, nuclear membranes break down, spindle fibres begin to form.
Explanation
The correct answer is C.
Candidates should use the diagram and the detailed steps of mitosis to answer this question.
Cell biology – cell division


Images reference: https://cmdss.org/parent-guide/about-down-syndrome/types-syndrome/
Above are two diagrams of cell division, one shows normal cell division, and another shows a cell division pathway that results in Down Syndrome.
The stages of mitosis are written below in the wrong order:
• Interphase: the cell grows, performs routine life processes and prepares to divide.
• Cytokinesis: the cytoplasm splits in two and two cells are formed.
• Telophase: Spindle fibres breakdown, nuclear membrane forms and chromosomes begin to uncoil and form chromatin.
• Anaphase: Sister chromatids are pulled apart and move to the opposite poles of the cells.
• Metaphase: Sister chromatids line up at the centre of the cell.
• Prophase: chromosomes are visible, nuclear membranes break down, spindle fibres begin to form.
Explanation
The correct answer is B.
Candidates should breakdown the word nondisjunction to help them determine what it likely means whilst also using the diagram to aid them in their reasoning.
Cell biology – cell division


Images reference: https://cmdss.org/parent-guide/about-down-syndrome/types-syndrome/
Above are two diagrams of cell division, one shows normal cell division, and another shows a cell division pathway that results in Down Syndrome.
The stages of mitosis are written below in the wrong order:
• Interphase: the cell grows, performs routine life processes and prepares to divide.
• Cytokinesis: the cytoplasm splits in two and two cells are formed.
• Telophase: Spindle fibres breakdown, nuclear membrane forms and chromosomes begin to uncoil and form chromatin.
• Anaphase: Sister chromatids are pulled apart and move to the opposite poles of the cells.
• Metaphase: Sister chromatids line up at the centre of the cell.
• Prophase: chromosomes are visible, nuclear membranes break down, spindle fibres begin to form.
Explanation
The correct answer is A.
If candidates take the time to read the statements carefully, they will be able to determine the correct order of events.
 Guest
Medicmind Tutor
Guest
Medicmind Tutor
Sun, 08 May 2022 18:52:14
Nah, it's memory
Cell biology – cell division


Images reference: https://cmdss.org/parent-guide/about-down-syndrome/types-syndrome/
Above are two diagrams of cell division, one shows normal cell division, and another shows a cell division pathway that results in Down Syndrome.
The stages of mitosis are written below in the wrong order:
• Interphase: the cell grows, performs routine life processes and prepares to divide.
• Cytokinesis: the cytoplasm splits in two and two cells are formed.
• Telophase: Spindle fibres breakdown, nuclear membrane forms and chromosomes begin to uncoil and form chromatin.
• Anaphase: Sister chromatids are pulled apart and move to the opposite poles of the cells.
• Metaphase: Sister chromatids line up at the centre of the cell.
• Prophase: chromosomes are visible, nuclear membranes break down, spindle fibres begin to form.
Explanation
The correct answer is D.
As nondisjunction refers to the failure of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate it must occur in Anaphase.
Cell structure
Below is a diagram of a nerve cell.
Dendrites receive the message from a cell or stimulus, this is then conducted down the axon to the terminal button where it is transmitted to another cell. Myelin, produced by schwann cells, aids conduction and the nodes of Ranvier enable saltatory conduction to transpire.
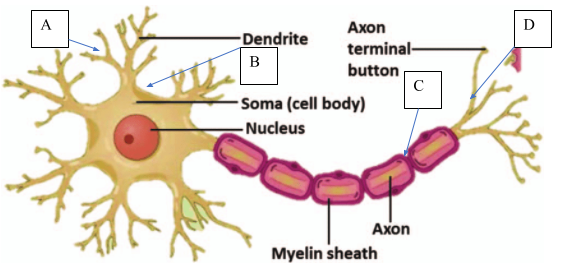
Image reference: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Nerve-cell-structure-unless-CC-License-in-place-see-abstract_fig3_270603738
Explanation
The correct answer is C.
Myelin is stated as being a property that aids conduction, therefore loss of it will reduce conduction efficacy eliminating answer A. Answers B and D do not make sense and are incorrect.
Cell structure
Below is a diagram of a nerve cell.
Dendrites receive the message from a cell or stimulus, this is then conducted down the axon to the terminal button where it is transmitted to another cell. Myelin, produced by schwann cells, aids conduction and the nodes of Ranvier enable saltatory conduction to transpire.

Image reference: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Nerve-cell-structure-unless-CC-License-in-place-see-abstract_fig3_270603738
Explanation
The correct answer is D.
Answer B is the function of the dendrites, answer A is incorrect as schwann cells produce myelin and the second half of the statement is incorrect. Answer C is not correct as it does not make sense for storage of chemical signals. Answer D is the correct answer.
Cell structure
Below is a diagram of a nerve cell.
Dendrites receive the message from a cell or stimulus, this is then conducted down the axon to the terminal button where it is transmitted to another cell. Myelin, produced by schwann cells, aids conduction and the nodes of Ranvier enable saltatory conduction to transpire.

Image reference: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Nerve-cell-structure-unless-CC-License-in-place-see-abstract_fig3_270603738
Explanation
The correct answer is C.
Candidates should be able to infer from the paragraph above the diagram that the nodes of Ranvier are most likely to be present on the cell axon.
Cell structure
Below is a diagram of a nerve cell.
Dendrites receive the message from a cell or stimulus, this is then conducted down the axon to the terminal button where it is transmitted to another cell. Myelin, produced by schwann cells, aids conduction and the nodes of Ranvier enable saltatory conduction to transpire.

Image reference: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Nerve-cell-structure-unless-CC-License-in-place-see-abstract_fig3_270603738
Explanation
The correct answer is B.
A, C and D do not make sense as options and are incorrect.
 Connor
Medicmind Tutor
Connor
Medicmind Tutor
Mon, 29 Aug 2022 13:53:07
Poorly worded. If this referred to one of the two pathways in the basal ganglia, C and D would be correct. (I chose C because i predicted that the author had very little neuroscience knowledge) It's best to think of this as postsynaptic inhibition.
Endocrinology
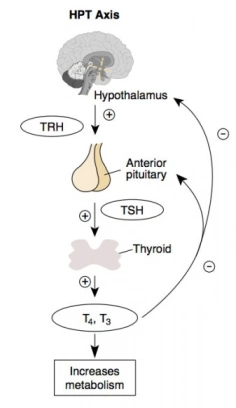
Image reference: https://easyhealth101.wordpress.com/2014/03/19/thyroid-to-burn-or-not-to-burn/
Explanation
The correct answer is A.
A drop in metabolism would result in fatigue.
Endocrinology

Image reference: https://easyhealth101.wordpress.com/2014/03/19/thyroid-to-burn-or-not-to-burn/
Explanation
The correct answer is D.
A productive tumour in the anterior pituitary would produce high levels of TSH, thus eliminating option A. Answer B is eliminated because T3 and T4 would be elevated in the presence of excessive TSH. As this axis works on negative feedback TRH would be reduced. Thus answer D is correct.
Endocrinology

Image reference: https://easyhealth101.wordpress.com/2014/03/19/thyroid-to-burn-or-not-to-burn/
Explanation
The correct answer is C.
A low T3 and T4 would stimulate the axis thus causing a rise in both TRH and TSH.
Endocrinology

Image reference: https://easyhealth101.wordpress.com/2014/03/19/thyroid-to-burn-or-not-to-burn/
Explanation
The correct answer is B.
Excessive metabolism would lead to weight loss.
Homeostasis
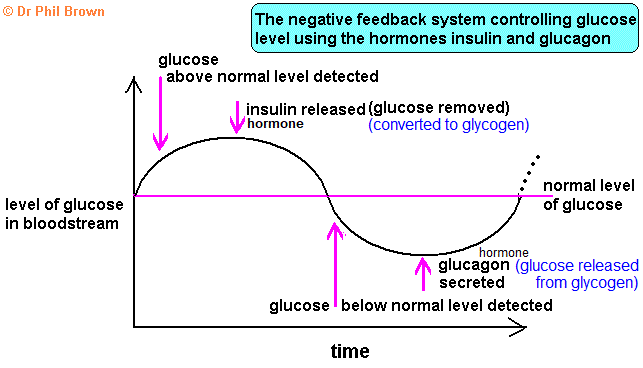
Image reference: https://docbrown.info/ebiology/homeostasis2.htm
Relevant information: insulin is secreted from beta cells in the pancreas. Glucagon is released from the alpha cells of the pancreas.
Explanation
The correct answer is B.
The diagram shows that insulin is secreted in high glucose states, the other statements contain inaccuracies.
Homeostasis

Image reference: https://docbrown.info/ebiology/homeostasis2.htm
Relevant information: insulin is secreted from beta cells in the pancreas. Glucagon is released from the alpha cells of the pancreas.
Explanation
The correct answer is C.
Glucose is a sugar; sugars are the components of carbohydrates therefore C is correct.
Homeostasis

Image reference: https://docbrown.info/ebiology/homeostasis2.htm
Relevant information: insulin is secreted from beta cells in the pancreas. Glucagon is released from the alpha cells of the pancreas.
Explanation
The correct answer is B.
Blood sugar would be lowest prior to breakfast when the individual has not eaten for many hours.
 Cathy
Medicmind Tutor
Cathy
Medicmind Tutor
Thu, 01 Sep 2022 23:52:26
would that be midnight when the blood glucose decreases but glucagon has not been released yet?
Homeostasis

Image reference: https://docbrown.info/ebiology/homeostasis2.htm
Relevant information: insulin is secreted from beta cells in the pancreas. Glucagon is released from the alpha cells of the pancreas.
Explanation
The correct answer is A.
Answers C and D are incorrect statements and B cannot be proven based on the information above.
Biology Questions Part 2 Review Screen
Instructions
Below is a summary of your answers. You can review your questions in three (3) different ways.
The buttons in the lower right-hand corner correspond to these choices:
1. Review all of your questions and answers.
2. Review questions that are incomplete.
3. Review questions that are flagged for review. (Click the 'flag' icon to change the flag for review status.)
You may also click on a question number to link directly to its location in the exam.
Biology Questions Part 2 Section
Final Answer Review Screen
Instructions
This review section allows you to view the answers you made and see whether they were correct or not. Each question accessed from this screen has an 'Explain Answer' button in the top left hand side. By clicking on this you will obtain an explanation as to the correct answer.
At the bottom of this screen you can choose to 'Review All' answers, 'Review Incorrect' answers or 'Review Flagged' answers. Alternatively you can go to specific questions by opening up any of the sub-tests below.
Biology Questions Part 2 Section
TI-108
Let's get acquainted ?
What is your name?
Nice to meet you, {{name}}!
What is your preferred e-mail address?
Nice to meet you, {{name}}!
What is your preferred phone number?
What is your preferred phone number?
Just to check, what are you interested in?
When should we call you?
What time works best for you? (UK Time)
How many hours of 1-1 tutoring are you looking for?
My WhatsApp number is...
For our safeguarding policy, please confirm...
For our safeguarding policy, please confirm...
Which online course are you interested in?
What is your query?
SubmitYou can apply for a bursary by clicking this link
https://www.medicmind.co.uk/medic-mind-foundation/Sure, what is your query?
SubmitLoading...
Thank you for your response.
We will aim to get back to you within 12-24 hours.
Lock in a 2 Hour 1-1 Tutoring Lesson Now
If you're ready and keen to get started click the button below to book your first 2 hour 1-1 tutoring lesson with us. Connect with a tutor from a university of your choice in minutes. (Use FAST5 to get 5% Off!)
Buy Now for £70