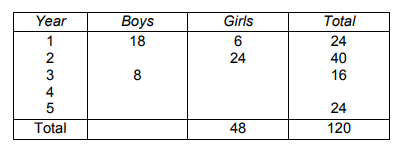
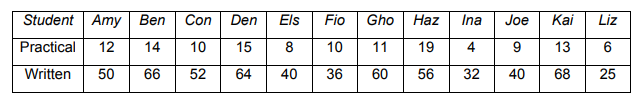
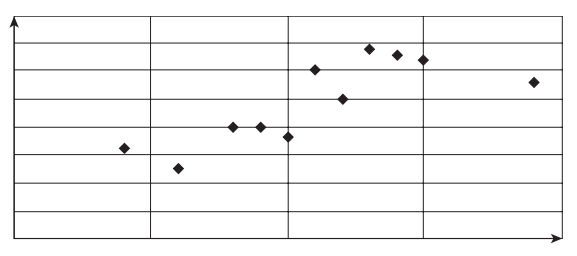
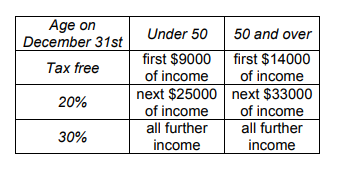
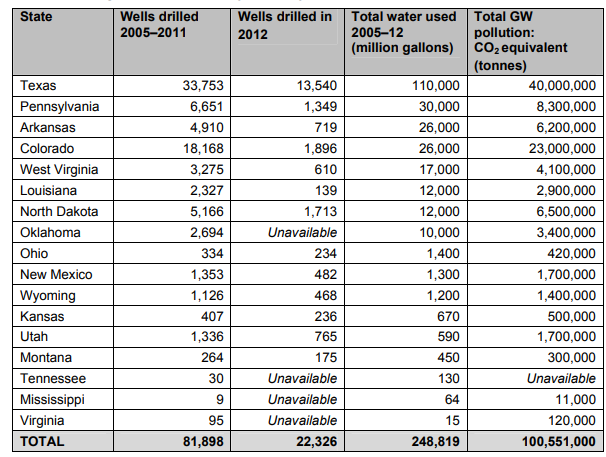
Fracking in the US 2005–2012
The oil and gas industry has increasingly turned to hydraulic fracturing – known as ‘fracking’ – in a highly polluting effort to unlock oil and gas in underground shale beds across the United States. Fracking is already underway in 17 states, with more than 100,000 wells drilled since 2005.
Water used
Since 2005, fracking has used nearly 250 billion gallons of water across the nation (see the Table below). The greatest total water consumption occurred in Texas, at the same time as the state was struggling with extreme drought. In Colorado the amount of water used for fracking was enough to meet the water needs of nearly 200,000 households in the state for a year.
Chemicals used
Fracking fluid consists of water mixed with chemicals such as benzene that is pumped underground to frack wells. Although in percentage terms chemicals are a small component of fracking fluid, the total volume of chemicals used is immense. According to the oil and gas industry, 99.2% (by volume) of fracking fluid is water and the other 0.8% is a mix of chemicals. These can enter drinking water supplies from the well, or in the wastewater disposal process.
Global warming (GW) pollution released
Completion of fracking wells from 2005 to 2012 produced global warming pollution equal to the CO2 emissions from 28 coal-fired power plants in a year.
Variation
Both water consumption and pollution levels varied sharply from state to state.
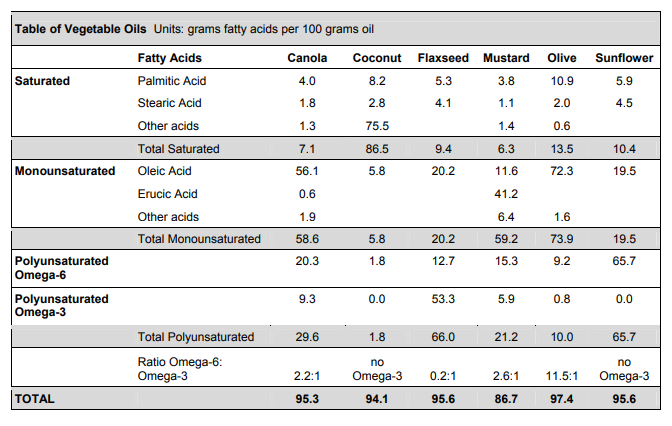
Table: Fracking states (ordered by quantity of water used)
Which of the following statements can be concluded from the information in the table and the text?
1 The fracking fluids used in Texas from 2005 to 2012 contained 880 million gallons of chemicals, with the risk of contaminating drinking water.
2 A typical coal-fired power station in the US emits approximately 36,000,000 tonnes of CO2 in one year.
3 A typical Colorado household needs around 130,000 gallons of water per year.